SMART App Launch Integration
This page provides implementation guidance on how to integrate your SMART on FHIR App (SMART App) with the MediRecords Patient Management System (PMS).
MediRecords implements SMART App Launch 2.2.0 for launching third-party SMART Apps using the EHR Launch flow.
As part of the EHR Launch flow, an opaque handle to the MediRecords user’s launch context (e.g. user, patient, consultation) is passed as a parameter of the SMART App’s launch URL.
The SMART App forwards this launch parameter in the authorization request to the MR Authorization Server and subsequently receives the associated launch context data from the MR Authorization Server in the token response.
SMART App Actors
The following actors are involved in the SMART App Launch process:
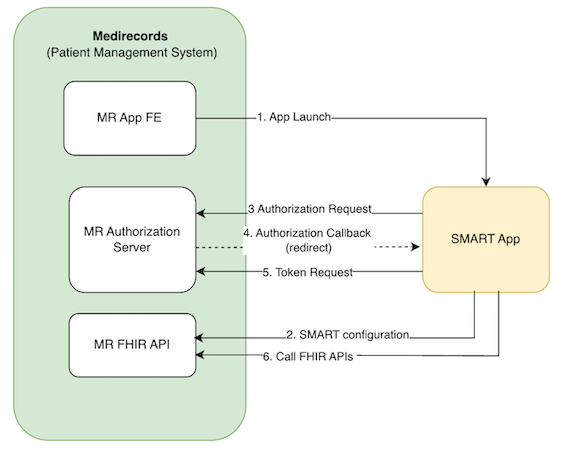
MR App FE
The Front End (browser-based) component of the MediRecords PMS that the user (e.g. clinician) is logged into.
It allows a user to launch the SMART App and provides the launch context to the App.
MR Authorization Server
The authorization server that handles OAuth 2.0 authorisation requests and issues access tokens.
It allows the SMART App to request authorisation from the user to access MediRecords patient information using the MR FHIR API.
MR FHIR API
The FHIR API that provides access to MediRecords patient information in the context of the MediRecords user and patient when the App was launched.
It allows the SMART App to read and write FHIR resources using the access token obtained from the MR Authorization Server.
SMART App
The third-party SMART on FHIR client application that is launched from MR App FE.
It uses the launch context to request authorisation from the user and access FHIR resources from the MR FHIR API.
Supported capabilities
The MediRecords SMART App Launch implementation is based on the SMART on FHIR Clinician Access for EHR Launch capability set, and supports the following capabilities as described in SMART App Launch Conformance Capabilities:
- launch-ehr
- client-public
- context-ehr-patient
- context-ehr-encounter
- permission-user
- permission-patient
- sso-openid-connect
- permission-v2
- permission-v1
The full list of capabilities currently supported by the MediRecords system can be retrieved from the smart-configuration endpoint.
SMART App Registration
Before a SMART App can be launched from MediRecords, the SMART App must be registered in the MR Authorization Server.
This is to ensure that only trusted applications can be authorised to access data from MediRecords.
MediRecords requires the following information to register and launch the SMART App:
- launch URL - the SMART App URL that MediRecords will use to launch the SMART App.
- redirect_uri - the SMART App URL that the MR Authorization Server will redirect to after the user authorizes the SMART App.
- scopes - the scopes that the SMART App is requesting authorization. See supported scopes for more information.
- client name - the name of the SMART App.
- launch_context parameters - the launch context parameters that the SMART App requires (e.g. patient, encounter, fhirUser).
Once registered, the SMART App will be assigned a client ID that it needs to provide in the authorization request.
SMART App EHR Launch Flow
The following diagram illustrates the SMART App EHR Launch flow.
The SMART App is launched by a user (e.g. clinician) within the MR App FE.
The SMART App initiates an OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow to gain an access token for authorizing access to FHIR resources from the MR FHIR API.
Preconditions:
- User is Logged into MR App FE
- The user launches the SMART App by clicking a button or menu item in the MR App FE
- MR App FE stashes launch context identified by an opaque identifier
- MR App FE displays an embedded iFrame (or new browser tab) with the SMART App’s launch URL.
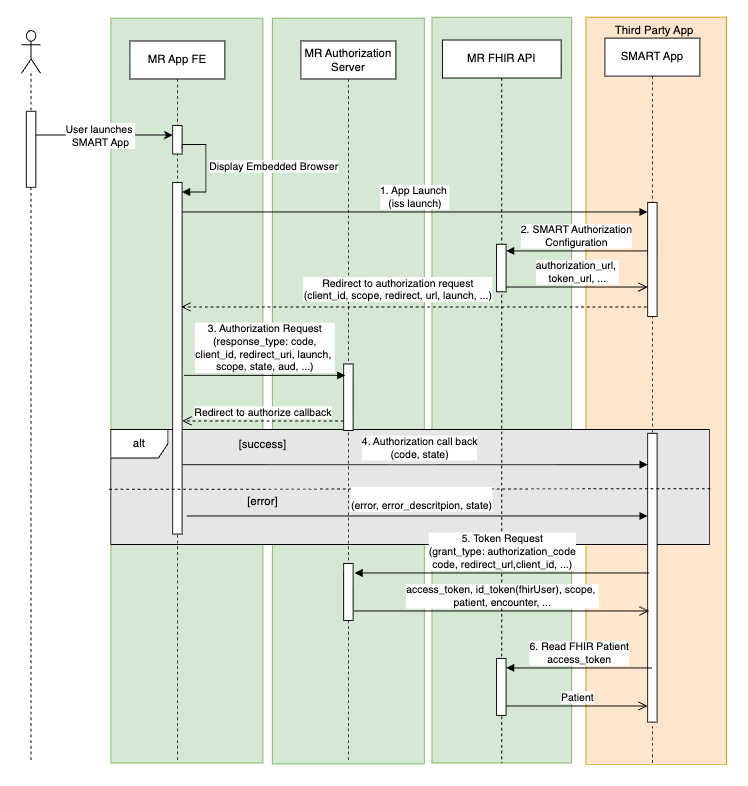
EHR Launch Flow:
- App Launch
- MR App FE initiates the app launch by calling the SMART App’s launch URL, including:
- iss: The FHIR base URL of the MR FHIR API
- launch: An opaque identifier representing the launch context
- The SMART App receives these parameters via its launch endpoint.
- SMART Authorization Configuration: smart-configuration endpoint
- The SMART App uses the iss (FHIR base URL) to retrieve the authorization configuration from the
.well-known/smart-configuration endpoint.
- This includes discovering:
- authorization endpoint
- token endpoint
- Authorization Request: authorize endpoint
- The SMART App constructs an authorization request to the authorization endpoint, including:
- client_id, redirect_uri, scope, state, and launch (the opaque id from step 1).
- The SMART App is redirected to the MR Authorization Server to authorize the SMART App.
- Authorization Callback
- On success, the response of the MR Authorization Server is to redirect back to the SMART App’s redirect_uri with:
- code: The authorization code
- state: Must be verified by the SMART App
- On error, the response also redirects back with error parameters.
- Token Request: token endpoint
- The SMART App sends a POST request to the token endpoint of the MR Authorization Server to exchange the authorization code for an access token. The request includes the following parameters:
- client_id, code, redirect_uri, and grant_type=authorization_code.
- The MR Authorization Server responds with an access token (and optionally a refresh token) and ID token.
- Read FHIR Patient
- The SMART App uses the access_token to invoke FHIR API requests to the MR FHIR API. Typically, this starts with a Read Patient request with the ID provided in the
patient launch context element returned in the token response.
Retrieving fhirUser reference from ID Token
The Token response contains an ID token which is a JSON Web Token (JWT) containing claims about the authentication event and the user.
To retrieve the fhirUser ID, the SMART App needs to decode the ID token and extract the relevant claim from the payload.
The ID token is base64url-encoded and signed by the authorization server, the SMART App should verify the signature to ensure the token’s integrity and authenticity.
It consists of three parts:
- JWS Protected Header - contains metadata about the token, such as the signing algorithm used.
- JWS Payload - contains the claims about the user and authentication event.
- The payload includes standard claims such as:
- iss: issuer identifier
- sub: subject identifier (user ID)
- aud: audience (client ID of the SMART App)
- exp: expiration time
- iat: issued at time
- It also includes SMART-specific claims such as:
- fhirUser: the URL of the FHIR resource representing the user (e.g. Practitioner/123)
- JWS Signature - used to verify the authenticity and integrity of the token.

